Lesson 9: Project - Designing an App Part 4
Project | App Lab
Overview
Students continue working on their apps. Halfway through class the focus of the lesson shifts to getting feedback. Students watch other groups test their apps and collect feedback that will be used to make updates.
Purpose
This lesson reinforces the importance of feedback in the process of developing software. Feedback and testing help make sure that an app actually works for lots of people and in the context in which it will be used. This process also reinforces the importance of making iterative improvements in making software.
Agenda
Lesson Modifications
Warm Up (5 mins)
Activity (30 mins)
Wrap Up (10 mins)
View on Code Studio
Objectives
Students will be able to:
- Test an app's functionality by attempting to use features and behavior described in a program specification
- Provide effective feedback on the functionality or usability of an app
- Iteratively improve an app based on feedback
Preparation
- Make sure students have access to their App Development Planning Guides
Links
Heads Up! Please make a copy of any documents you plan to share with students.
For the Teachers
- CSP Unit 3 - Intro to App Design - Presentation
For the Students
- App Development Planning Guide - Activity Guide
Teaching Guide
Lesson Modifications
 Attention, teachers! If you are teaching virtually or in a socially-distanced classroom, please read the full lesson plan below, then click here to access the modifications.
Attention, teachers! If you are teaching virtually or in a socially-distanced classroom, please read the full lesson plan below, then click here to access the modifications.
Warm Up (5 mins)
Discussion Goal
Goal: This is an optional prompt if your class situation requires it. If you believe your students need more time to work on their apps then move right into work time. This prompt, however is designed to get students thinking early about the differences between useful and unhelpful feedback. For example, students may note that...
- Good feedback:
- Specific information beyond "it's great".
- Explains why something needs work
- Bad Feedback:
- Is overly negative without constructive feedback
- Does not go into enough detail
Prompt: Think of times when you've received helpful feedback on school work, a hobby, or a sport.
- What makes good feedback?
- What makes bad feedback?
Remarks
Today we're going to keep working on our apps, but we're also going to be getting feedback from our classmates. Let's get to it!
Activity (30 mins)
Group: Place students back in pairs with their project partners.
Work Time - 25 mins
Teaching Tip
Review Pair Programming: You may want to reuse the slides from the previous lesson to remind students of their Pair Programming roles.
Encourage Debugging Practices: Continue to encourage students to use the debugging practices they learned in previous lessons and normalize and celebrate debugging as a part of programming
Remarks
Circulate: Direct students to Code Studio to continue working on their apps.
Testing and Feedback - 10 mins
Distribute: Direct students back to the App Development Planning Guide - Activity Guide.
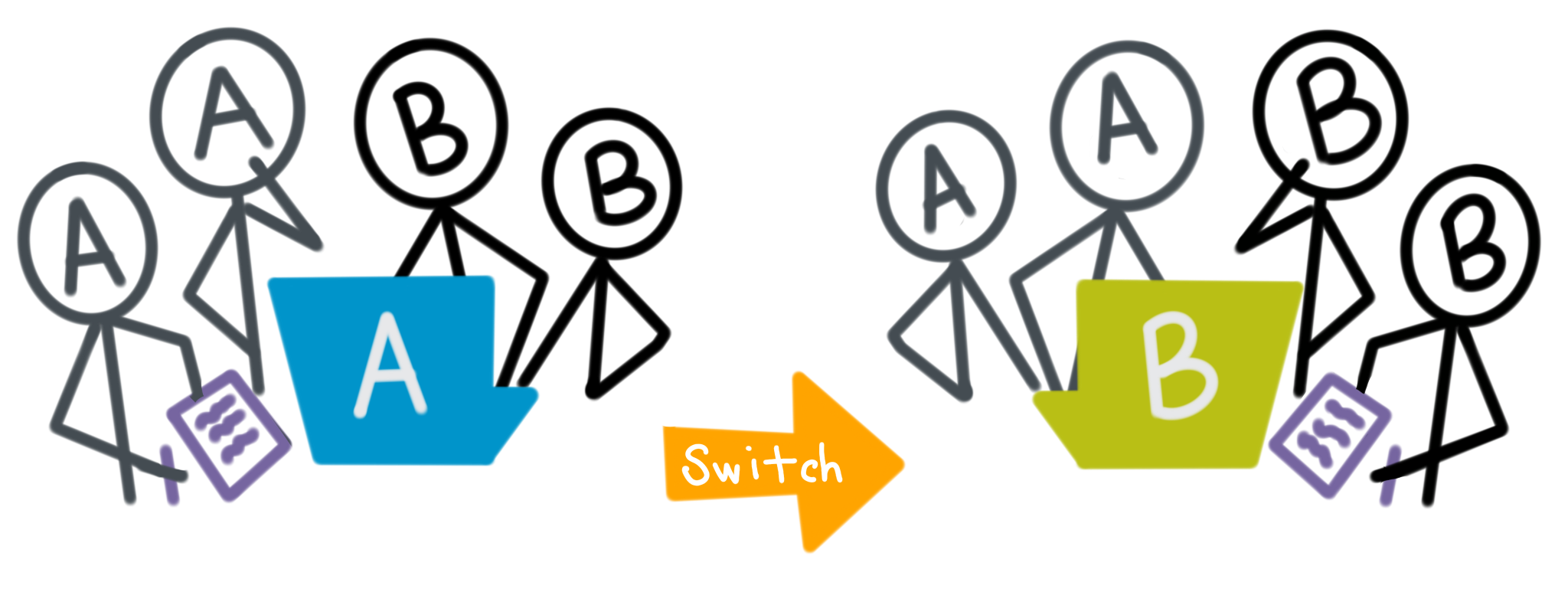
Step 6: Groups swap apps and gather feedback. It is ok to move ahead to this section even if students are not done with their apps yet.
Here's what you should observe:
- Group A lets Group B test their app.
- Group A watches Group B use the app, and writes down improvements that come to mind.
- Group A interviews Group B asking for specific improvements Group A can make. This may be different than what Group A came up with during the observation. These improvements are written down in the Activity Guide.
- Group A and B swap and now Group A tests Group B's app while Group B watches.
- After this, mix up the group pairings and repeat the steps above.
Wrap Up (10 mins)
Remarks
Step 7: Now return to your stations and pick at least one improvement to make to their app based on feedback. Write this down in the Planning Guide in Step 7.
Discussion Goal
Goal: Use this prompt as time allows. The goal is to reinforce the importance of feedback in the development of good software. Possible answers include:
- Another person may find a bug that you have been overlooking
- Something that seems obvious to you is not obvious to the user
- Even if the app isn't finished, feedback can help guide the next steps
Prompt: Why is it important to get feedback from others while building your app? What is the value of getting this feedback even if you aren't finished with your app?
Remarks
Feedback and testing are important parts of making good software. They ensure that our apps actually work the way we designed them, and they help us make gradual improvements. Tomorrow you'll have a chance to make some final touches on your app before we submit them!
Standards Alignment
View full course alignment
CSTA K-12 Computer Science Standards (2017)
AP - Algorithms & Programming
- 3A-AP-16 - Design and iteratively develop computational artifacts for practical intent, personal expression, or to address a societal issue by using events to initiate instructions.
- 3A-AP-19 - Systematically design and develop programs for broad audiences by incorporating feedback from users.
- 3A-AP-21 - Evaluate and refine computational artifacts to make them more usable and accessible.
- 3A-AP-22 - Design and develop computational artifacts working in team roles using collaborative tools.
- 3A-AP-23 - Document design decisions using text, graphics, presentations, and/or demonstrations in the development of complex programs.
CSP2021
CRD-1 - Incorporating multiple perspectives
CRD-1.A - Explain how computing innovations are improved through collaboration.
- CRD-1.A.5 - Consultation and communication with users are important aspects of the development of computing innovations.
CRD-1.B - Explain how computing innovations are developed by groups of people.
- CRD-1.B.1 - Online tools support collaboration by allowing programmers to share and provide feedback on ideas and documents.
CRD-2 - Developers create and innovate using an iterative design process
CRD-2.E - Develop a program using a development process.
- CRD-2.E.3 - A development process that is iterative requires refinement and revision based on feedback, testing, or reflection throughout the process. This may require revisiting earlier phases of the process.
CRD-2.J - Identify inputs and corresponding expected output or behaviors that can be used to check the correctness of an algorithm or program.
- CRD-2.J.1 - In the development process, testing uses defined inputs to ensure that an algorithm or program is producing the expected outcomes. Programmers use the results from testing to revise their algorithms or programs.
- CRD-2.J.3 - Program requirements are needed to identify appropriate defined inputs for testing.
