Lesson 28: End of Course Project
Overview
The next five lessons provide an opportunity for students to put their coding skills to use in a capstone project. This project will help individuals gain experience with coding and produce an exemplar to share with peers and loved ones. This is intended to be a multi-lesson or multi-week project where students spend time brainstorming, learning about the design process, building, and then presenting their final work.
In the "Explore" stage, students will play around with pre-built Artist and Sprite Lab programs for inspiration. Next, students will learn about the design process and how to implement it in their own projects. They will then be given the space to create their own project in Artist, Sprite Lab, or any other interface that you are comfortable providing. (This is likely the longest stage of the project.) Students will then revise their code after testing and peer review. Finally, students will be able to present their finished work to their classmates.
Purpose
Students may be ready to jump straight into building their projects, but this lesson will help shape their ideas into plans. This structure will keep the dreamers grounded and illuminate a path for those feeling left in the dark. Provide students with ample time to build and revise their projects. The trial and error inevitably involved in this lesson will teach problem solving and persistence.
Agenda
Explore Project Ideas (45 min)
Build Your Project (45 min)
Extension Activity
View on Code Studio
Objectives
Students will be able to:
- Learn to plan in advance for an ongoing assignment.
- Be able to explain how system limitations can affect project design.
- Describe how compromise can help keep a project on track and inspire creativity.
- Draft and implement plans to resolve any issues in their code.
- Articulate the design process and how it helped shape the finished culminating project.
Preparation
- Spend time making your own project with both the Artist and Sprite Lab. Familiarize yourself with the capabilities and limitations of each tool.
- Modify the rubric to fit your class goals and print out a copy for each student.
- Modify the project design worksheet to fit your class and print one packet for each student.
Links
Heads Up! Please make a copy of any documents you plan to share with students.
For the Teachers
- Design Process - Teacher Prep Guide
- Final Project Design - Worksheet
- CS Fundamentals Final Project - Rubric
Vocabulary
- Define - Figure out the details of the problems that you are trying to solve
- Prepare - Research, plan, and acquire materials for the activity you are about to do
- Reflect - Carefully think back on something with the intention of improving the outcome in the future
- Try - Attempt to do something
Support
Report a Bug
Teaching Guide
Explore Project Ideas (45 min)
Example Projects
Goal: This part of the process is an exploration. Students will sit down with a stage full of example projects to remix and learn. Not only will this give students an idea of what is possible, it will also help them see the limitations of the tool.
Give students a day to play with and remix the projects found on Code Studio. Have them use their journals (or notebook paper) to keep track of thoughts and ideas as they go.
This activity should be done in the same pairs/groups that will be working on projects together over the next several lessons.
Make sure your class understands that they will be spending the next several weeks working with projects of their own, so they should pay close attention to how these programs were written, as well as the concepts that they use.
Build Your Project (45 min)
Goal: Students will build a project.
Students should head to the computers to start bringing their projects to life.
This process will come complete with plenty of trial and error. Projects are likely to become truncated versions of their original ideas (if not morphed altogether). Remind students that this kind of compromise is common in software design, but they need to be sure to document the reasons for the changes in their product.
- Example Projects
- 1
Student Instructions
Project Examples
You are about to start your final project. Before you begin, spend some time looking at the example projects.
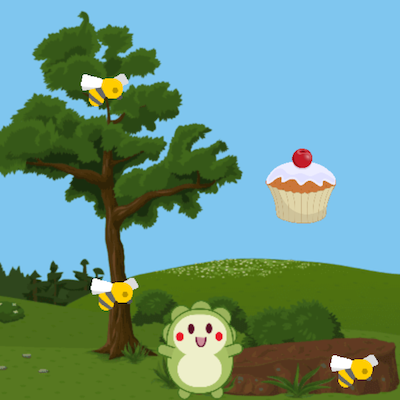
Sprite Lab
| Cupcake Game (Sprite Lab) | Helicopter Game (Sprite Lab) |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| Try adding text or a score to this game! | Try adding text or a score to this game! |
Artist
| Flowers (Artist) | Spiral (Arist) |
|---|---|
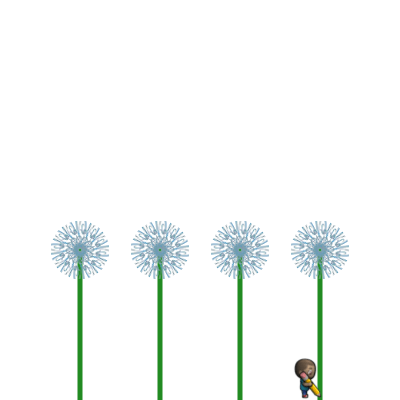 |
 |
| Let's get creative with variables! | Let's get creative with For Loops! |
- Sprite Lab Project
- 2
Student Instructions
- Artist Project
- 3
Student Instructions
Standards Alignment
View full course alignment
CSTA K-12 Computer Science Standards (2017)
AP - Algorithms & Programming
- 1B-AP-08 - Compare and refine multiple algorithms for the same task and determine which is the most appropriate.
- 1B-AP-09 - Create programs that use variables to store and modify data.
- 1B-AP-10 - Create programs that include sequences, events, loops, and conditionals.
- 1B-AP-11 - Decompose (break down) problems into smaller, manageable subproblems to facilitate the program development process.
- 1B-AP-12 - Modify, remix or incorporate portions of an existing program into one's own work, to develop something new or add more advanced features.
- 1B-AP-13 - Use an iterative process to plan the development of a program by including others' perspectives and considering user preferences.
- 1B-AP-14 - Observe intellectual property rights and give appropriate attribution when creating or remixing programs.
- 1B-AP-15 - Test and debug (identify and fix errors) a program or algorithm to ensure it runs as intended.
- 1B-AP-16 - Take on varying roles, with teacher guidance, when collaborating with peers during the design, implementation and review stages of program development.
- 1B-AP-17 - Describe choices made during program development using code comments, presentations, and demonstrations.
Cross-curricular Opportunities
This list represents opportunities in this lesson to support standards in other content areas.
Common Core English Language Arts Standards
L - Language
- 4.L.6 - Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate general academic and domain-specific words and phrases, including those that signal precise actions, emotions, or states of being (e.g., quizzed, whined, stammered) and that are basic to a particular topic (e.g
SL - Speaking & Listening
- 4.SL.1 - Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 4 topics and texts, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly.
W - Writing
- 4.W.6 - With some guidance and support from adults, use technology, including the Internet, to produce and publish writing as well as to interact and collaborate with others; demonstrate sufficient command of keyboarding skills to type a minimum of one page in a
Common Core Math Standards
MP - Math Practices
- MP.1 - Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them
- MP.2 - Reason abstractly and quantitatively
- MP.4 - Model with mathematics
- MP.5 - Use appropriate tools strategically
- MP.6 - Attend to precision
- MP.7 - Look for and make use of structure
- MP.8 - Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
Next Generation Science Standards
ETS - Engineering in the Sciences
ETS1 - Engineering Design
- 3-5-ETS1-1 - Define a simple design problem reflecting a need or a want that includes specified criteria for success and constraints on materials, time, or cost.
- 3-5-ETS1-2 - Generate and compare multiple possible solutions to a problem based on how well each is likely to meet the criteria and constraints of the problem.
