Lesson 12: The Big Event Jr.
Overview
Events are a great way to add variety to a pre-written algorithm. Sometimes you want your program to be able to respond to the user exactly when the user wants it to. That is what events are for.
Purpose
Today, students will learn to distinguish events from actions. The students will see activities interrupted by having a "button" pressed on a paper remote. When seeing this event, the class will react with a unique action. Events are widely used in programming and should be easily recognizable after this lesson.
Agenda
Warm Up (15 min)
Main Activity (15 min)
Wrap Up (10 min)
Assessment (10 min)
Extended Learning
View on Code Studio
Objectives
Students will be able to:
- Repeat commands given by an instructor.
- Recognize actions of the teacher as signals to initiate commands.
- Practice differentiating pre-defined actions and event-driven ones.
Preparation
- Watch the The Big Event - Teacher Video.
- Print one The Big Event (Courses A, B) - Controller Image.
- Print one The Big Event - Assessment for each student.
- Make sure each student has a Think Spot Journal - Reflection Journal.
Links
Heads Up! Please make a copy of any documents you plan to share with students.
For the Teachers
- The Big Event - Teacher Video
- The Big Event - Assessment Answer Key
For the Students
- The Big Event - Unplugged Video (download)
- Feeling Faces - Emotion Images
- The Big Event (Courses A, B) - Controller Image
- The Big Event - Assessment
- Think Spot Journal - Reflection Journal
Vocabulary
- Event - An action that causes something to happen.
Support
Report a Bug
Teaching Guide
Warm Up (15 min)
Vocabulary
This lesson has one new and important vocabulary word:
Event - Say it with me: E-vent
An action that causes something to happen
A Series of Events
- Prep your class to answer a question:
- "I'm going to ask you a question. I want you to raise your hand if you want me to call on you for the answer."
- Ask a simple question that most of your students should be able to answer, such as:
- How many thumbs do I have?
- What is bigger, a bird or a horse?
- Call on a student who has their hand raised and let them give their answer.
- Upon finishing that display, ask the class how you knew that the student wanted you to call on them.
- Your class will likely mention the raising of the hand.
- Explain to everyone that when students raise their hand, it is an "event" that causes you to know that they want to be called on.
- Ask the class if they can think of any other events that give signals.
- You may need to remind them that you're not talking about an event like a birthday party or a field trip.
- If they have trouble, you can remind them that an event is an action that causes something to happen.
- What about an alarm clock going off? What does that make happen?
- What about pressing "Start" on the microwave? What does that do?
- What about pressing the power button on your tv remote?
- Today, we're going to create programs with events.
Main Activity (15 min)
The Big Event
Lesson Tip
If your students seem confused, talk about their favorite games and all of the ways that they let the characters know what they're supposed to do. Point out how the game would be really boring if it ran from start to finish without any events required.
- Do you remember helping the Red, the Angry Bird find the pig?
- In that exercise, you knew in advance exactly where you wanted Red to end up, so you could make a program that took the bird from start to finish without any interruptions.
- In most real programs, we can't do that because we want to have options, depending on what the user needs.
- Say that I only want my character to move when my finger is on the screen of my phone. I would need to program the character to only move when I put my finger on the screen of my phone.
- Putting my finger on the screen would then become an "event" that tells my character to move.
In earlier lessons, we created algorithms that allowed us to control a friend or bird for several steps at a time. It was fun and useful, but what happens when you don’t know everything that you want your friend to do in advance? This is where events come in!
Directions:
- Project the Event Controller onto your classroom screen.
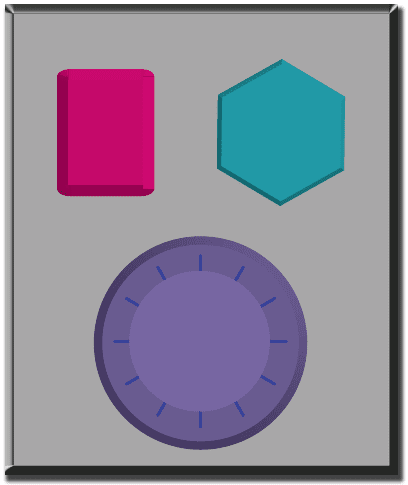
- Decide with your class what each button does. We suggest:
- Pink Button -> Say “Wooooo!”
- Teal Button -> “Yeah!”
- Purple Dial -> “Boom!”
- Practice tapping the buttons on the overhead and having your class react.
- Add some button sequences into the mix and have the students try to keep up with their sounds.
- Let your class know that every time you push a button, it is an “event” that lets them know what they are expected to do next.
- Get the class started on a planned task before interrupting them again with the buttons. We suggest:
- Counting to 10
- Singing “Old MacDonald”
- Once their plan is underway, interject button presses sporadically.
- Continue the blend until they understand the difference between actions that are guided by a plan and those that are event driven.
Wrap Up (10 min)
Flash Chat: What did we learn?
- Why do we need to be able to handle events in a program?
- What are some other kinds of events that you can think of?
Journaling
Journal Prompts:
- What was today’s lesson about?
- Draw one of the Feeling Faces - Emotion Images that shows how you felt about today's lesson in the corner of your journal page.
- Draw an event that caused an action today.
- Draw an action that was caused by an event that happened today.
Assessment (10 min)
The Big Event - Assessment
- Hand out the assessment activity and allow students to complete the activity independently after the instructions have been well explained.
- This should feel familiar, thanks to the previous activities.
Extended Learning
Use these activities to enhance student learning. They can be used as outside of class activities or other enrichment.
One Person's Event is Another One's Reaction
Assign each student an event to watch out for, and an appropriate reaction to that event. Chain the actions so that each child's reaction becomes an event that triggers the reaction of another student. Keep assigning until everyone has something to do and everyone makes someone react.
Eventopalooza
Break the class up into groups. Using the Events Controller, assign each group a different reaction to the same button. Do this for all three buttons, then watch the chaos!
Standards Alignment
View full course alignment
CSTA K-12 Computer Science Standards (2017)
AP - Algorithms & Programming
- 1A-AP-09 - Model the way programs store and manipulate data by using numbers or other symbols to represent information.
- 1A-AP-11 - Decompose (break down) the steps needed to solve a problem into a precise sequence of instructions.
Cross-curricular Opportunities
This list represents opportunities in this lesson to support standards in other content areas.
Common Core English Language Arts Standards
L - Language
- 1.L.6 - Use words and phrases acquired through conversations, reading and being read to, and responding to texts, including using frequently occurring conjunctions to signal simple relationships (e.g., because).
SL - Speaking & Listening
- 1.SL.1 - Participate in collaborative conversations with diverse partners about grade 1 topics and texts with peers and adults in small and larger groups.
- 1.SL.1.a - Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions (e.g., listening to others with care, speaking one at a time about the topics and texts under discussion).
- 1.SL.1.b - Build on others’ talk in conversations by responding to the comments of others through multiple exchanges.
- 1.SL.1.c - Ask questions to clear up any confusion about the topics and texts under discussion.
Common Core Math Standards
MP - Math Practices
- MP.1 - Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them
- MP.2 - Reason abstractly and quantitatively
- MP.6 - Attend to precision
- MP.7 - Look for and make use of structure
- MP.8 - Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
Next Generation Science Standards
ETS - Engineering in the Sciences
ETS1 - Engineering Design
- K-2-ETS1-1 - Ask questions, make observations, and gather information about a situation people want to change to define a simple problem that can be solved through the development of a new or improved object or tool.
- K-2-ETS1-2 - Develop a simple sketch, drawing, or physical model to illustrate how the shape of an object helps it function as needed to solve a given problem.
- K-2-ETS1-3 - Analyze data from tests of two objects designed to solve the same problem to compare the strengths and weaknesses of how each performs.
