Lesson 12: Arrays and For Loops
Overview
Using a for loop to iterate over all of the elements in an array is a really useful construct in most programming languages. In this lesson, students learn the basics of how a for loop can be used to repeat code, and then combine it with what they've already learned about arrays to write programs that process all elements in an array. Students use for loops to go through each element in a list one at a time without having to write code for each element. Towards the end of the lesson students will apply this with the colorLed list on the board to create an app that changes all of the LEDs each time a button is clicked.
Purpose
As students start using arrays more frequently, a common pattern emerges wherein you want to run some code on each element of an array. While for loops are a generally useful structure for repeating code, they are a particularly useful for iterating over an array. In this lesson we build on the understanding of arrays that students have developed in the last two lessons by introducing the for loop, which combines a variable, the counter pattern, and a conditional all in a single construct.
Agenda
Warm Up (5 min)
Activity (40 min)
Wrap Up
View on Code Studio
Objectives
Students will be able to:
- Modify the exit condition of a for loop to control how many times it repeats
- Use a for loop to iterate over an array
Vocabulary
- Array - A data structure in JavaScript used to represent a list.
- For Loop - Loops that have a predetermined beginning, end, and increment (step interval).
Introduced Code
Teaching Guide
Warm Up (5 min)
Run Code on All Elements of an Array
Discussion Goal
You shouldn't expect students to know how exactly a computer would do this, but to start thinking about what is needed to keep track of where you are in an array (the index), how you would know you've reached the end of the array (the array length), and how you might incrementally increase where you are in the list (the counter pattern).
Discuss: If you had a list full of all of your ToDos and you wanted the computer to print out each one, how might you do it? Don't worry about the specific code, focus on the what information your program would need to know and keep track of. Would your approach still work if you added or removed a ToDo from your list?
Remarks
Doing something to every element of an array is a really common problem in Computer Science, and figuring out how to solve this problem will let us write more efficient programs. Today we're going to focus on three things to help us with this problem
- Using the index to do something to elements in an array
- Keeping track of a counter so we can move through the elements of an array by index
- Using the length of an array to know when we've reached the end
Activity (40 min)
Arrays and For Loops
Transition: Send students to Code Studio
Wrap Up
Journal
Prompt: Have students reflect on their development of the five practices of CS Discoveries (Problem Solving, Persistence, Creativity, Collaboration, Communication). Choose one of the following prompts as you deem appropriate.
-
Choose one of the five practices in which you believe you demonstrated growth in this lesson. Write something you did that exemplified this practice.
-
Choose one practice you think you can continue to grow in. What’s one thing you’d like to do better?
-
Choose one practice you thought was especially important for the activity we completed today. What made it so important?
- Lesson Overview
- Student Overview
Student Instructions
Make a Prediction
Read through the code for this program and predict what will happen each time the button is clicked?
Student Instructions
Knowing When to Stop
If you clicked the button too many times in the last level, you got an error. Whenever you're writing code that repeats, you should think about when to stop repeating.
Do This
This program is similar to the previous one, but there is a conditional inside the event handler. You'll need to complete the conditional so that we don't try to toggle an LED that doesn't exist.
Would your code work without changes for a board with more or fewer LEDs? If not, could you modify it so it would?
- For Loops
- Student Overview
- CSD: For Loop_2018
- Student Overview
Student Instructions
Predict
What will print as a result of this loop?
Student Instructions
Looping Over Arrays
One of the most powerful ways to use a for loop is to loop over an array, running code on each item in the array. We can do this by using the for loop counter variable (usually i) as the index of your array.
Do This
This program should loop over the array buttons and do two things to each button - change the background color to red, and change the height to 50 px.
- Add a second
setPropertyblock inside the loop - Change the target to
buttons[i] - Set the "height" property to 50
Student Instructions
Array Length
In the last program we told the loop to run three times with the code for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++). This works, but we could write smarter programs by using the length of the array to decide how many times to loop.
Do This
Change the exit condition of this for loop so that it runs while i < buttons.length.
Student Instructions
Constructing a for loop from scratch
Now that you've had some practice modifying for loops to process arrays, let's see if you can do it yourself.
Do This
We've provided the design elements and an array to start with, but the rest is on you.
- Add an event handler to respond to the "thumbsup_button" being clicked
- Place a for loop inside the event handler
- Modify the exit condition of the for loop so that it will run until it gets to the end of the array
images - Inside your for loop change the current image to "icon://fa-thumbs-o-up"
Challenge: Can you add a second button that turns all of the images back to thumbs down?
Student Instructions
Turning all the Color LEDs On
Now that you know how to use a for loop to process all of the elements in an array, you can turn on all of the Color LEDs much more easily than before.
Do This
Over the next few levels, you'll create an app that will control all of the Color LEDs on your board. The first step is to wire up the button that turns all of the LEDs on. (Don't worry about the rest of the comments in the workspace. You'll work on those in later levels.)
- Add an event handler for "button_on"
- Place a for loop in your event handler that repeats until it reaches in the end of the array
colorLeds - Inside the for loop, call
colorLeds[i].on()to turn on the current color LED
Student Instructions
Turning all the Color LEDs Off
Now that you've got one button to turn the color LEDs on, you can make another turn them off.
Do This
Add an event handler to "button_off" with a for loop that turns each color LED off.
Student Instructions
Switching Colors with a Function
We could write a for loop for each different color that we want to set LEDs to, but that would be a lot of duplicate code that's almost the same. This is the perfect place to use a function with a parameter! You've seen and used functions with parameters before, but now you're going to make one from scratch.
Do This
Create a function called setLedsColor that takes a parameter color and uses it to change the color of all of the LEDs
- At the bottom of your program, drag out a function with parameter block
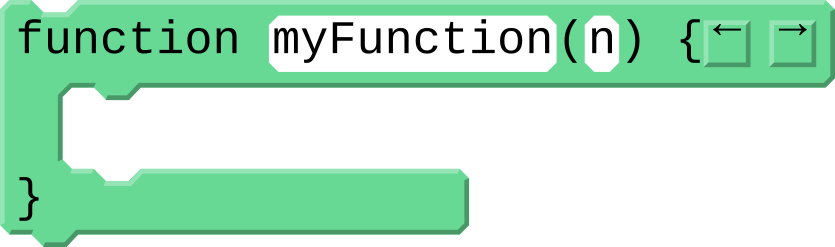
- Change the name from
myFunctiontosetLedsColor - Change the parameter name from
ntocolor - Inside your function, add a for loop that repeats until it reaches the end of
colorLeds - Inside your for loop, set the color of the current led to the parameter
color(eg.colorLeds[i].color(color)
We'll add event handlers that use this function in the next level, but for now you can test your function by your program and typing this into the debug console: setLedsColor("blue")
Student Instructions
Calling Your Function
Now that you've created a function that can behave differently based on the parameter it is passed, we can use it in multiple different event handlers to change the lights to different colors.
Do This
We'll start simple by just creating an event handler for "button_red"
- Create a new event handler to respond to "button_red"
- Inside your event handler, add a "call function with parameter" block

- Change the name from
myFunctiontosetLedsColor - Change the parameter from
nto "red" (note the quotation marks!) - Test your program, the "Red" button should turn all of your LEDs red
Student Instructions
Finish the App
If your red button worked, the only thing left is to call your new function when all of the remaining buttons is pressed.
Do This
For each of the remaining buttons (green, blue, and white):
- Create a new event handler
- Call your
setLedsColorfunction with the appropriate color ("green", "blue", or "white") - Test your program to make sure all of the buttons work
When you've got all of your buttons working properly, click "Submit" to turn your program in.
Student Instructions
Challenge: Add More Buttons
Extend the program by adding more buttons that change the board to different colors.
Do This
Add your new buttons in Design Mode and create event handlers to respond to your buttons and change the LED colors.
Student Instructions
Challenge: Color Patterns
Extend the program by adding more buttons that create different patterns of light.
Do This
Add your new buttons in Design Mode and create event handlers to respond to your buttons and change the LED colors.
Hint: As you design your patterns, consider whether a function with parameters could help simplify your program.
Student Instructions
Challenge: Music
Use what you learned in the Making Music lesson to make the board play music when the lights change.
Do This
Create some arrays of notes for different songs and add code to your event handlers to play your music.
Standards Alignment
View full course alignment
CSTA K-12 Computer Science Standards (2017)
AP - Algorithms & Programming
- 2-AP-11 - Create clearly named variables that represent different data types and perform operations on their values.
- 2-AP-12 - Design and iteratively develop programs that combine control structures, including nested loops and compound conditionals.
- 2-AP-13 - Decompose problems and subproblems into parts to facilitate the design, implementation, and review of programs.
- 2-AP-14 - Create procedures with parameters to organize code and make it easier to reuse.
- 2-AP-16 - Incorporate existing code, media, and libraries into original programs, and give attribution.
- 2-AP-17 - Systematically test and refine programs using a range of test cases.
- 2-AP-19 - Document programs in order to make them easier to follow, test, and debug.
CS - Computing Systems
- 2-CS-01 - Recommend improvements to the design of computing devices, based on an analysis of how users interact with the devices.
- 2-CS-02 - Design projects that combine hardware and software components to collect and exchange data.
- 2-CS-03 - Systematically identify and fix problems with computing devices and their components.
